

They tend to be low-grade and easier to target with treatments such as surgery and radiotherapy than diffuse glioma. New classifications published by the World Health Organisation (WHO) in 2016 meaning that it is officially known as a diffuse midline glioma.Ībout 20% of brainstem tumours are focal, meaning that they are localised (focused) in one area of the brain stem, usually the midbrain or medulla rather than the pons. It is usually referred to as a diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG), despite A grade 4 diffuse brainstem glioma is the most common form.Diffuse astrocytoma in the brain stem can be grade 2 or grade 3.Astrocytoma is a type of glioma that most “Diffuse” means that the tumour has spread out through the brain stem, in amongst healthy cells. What types of brainstem glioma are there?īrainstem gliomas are classified into a number of different types, with names primarily reflecting their position and spread, as well as the types of cells seen when a tumour sample is viewed through a microscope (histology). Grade 2 gliomas may sometimes transform to a higher grade over a number of years. In adults, brain stem gliomas tend to be low-grade and hence classified as grade 1 or grade 2. In children, brain stem gliomas can be low-grade (slow growing, grades 1 and 2) or high-grade (fast growing, grades 3 and 4), but unfortunately they are most often high-grade. Low-grade tumours are a slow-growing form of cancer, whilst high-grade tumours Are brain stem glioma tumours benign or cancerous?Īny tumour affecting the brain stem is likely to cause symptoms that cannot be considered “benign”, so tumours tend to be referred to as low-grade or high-grade.
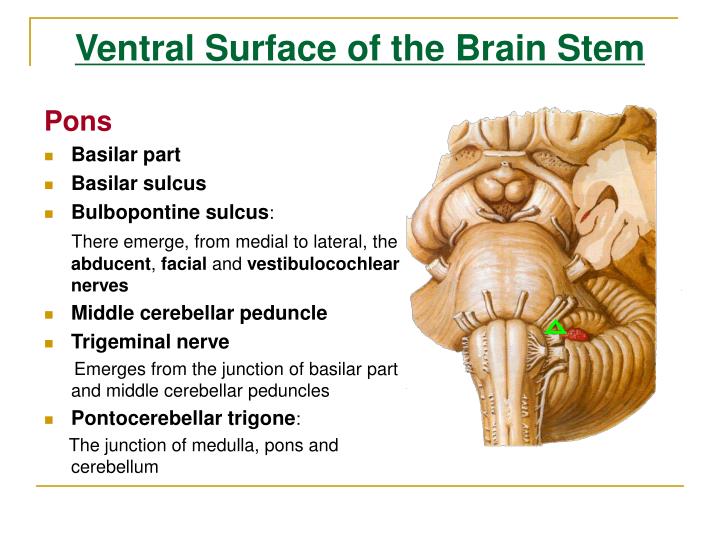
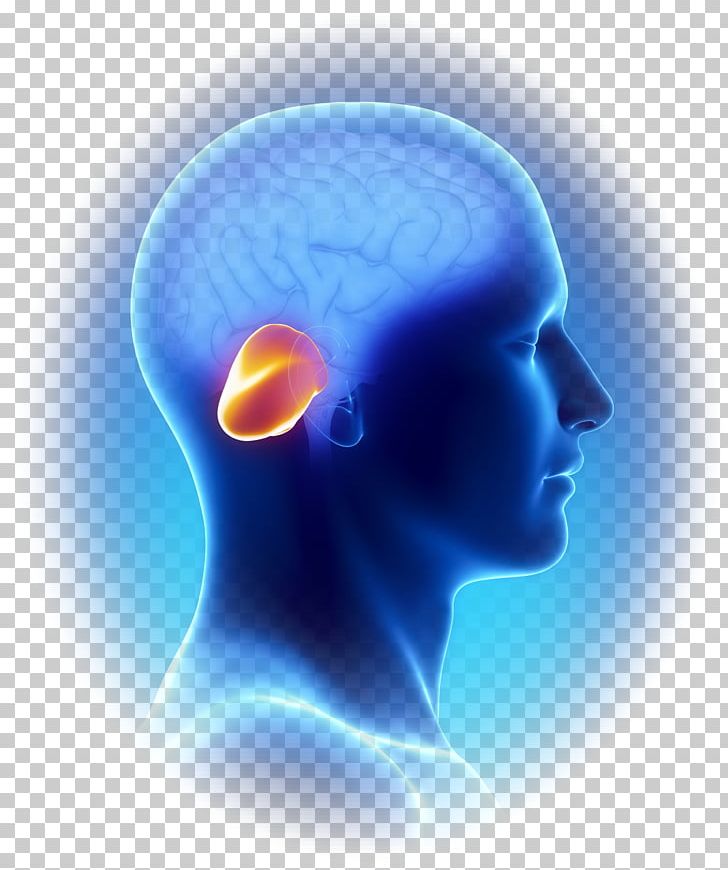
The brain stem also influences bodily functions that happen mainly subconsciously via the autonomic nervous system such as alertness, breathing, swallowing, blood pressure and heart rate. Most of the nerves that originate in the brain and spread out into the body pass through the brain stem. The brain stem acts as the main highway of communication between the brain, the spinal cord, and hence the rest of the body. The medulla oblongata, formed by the top of the spinal cord spreading out at the base of the brain.ĭiscover more about gliomas and glial cells here What does the brain stem do? Most brainstem gliomas arise in this particular part of the brain stem. The pons, which is found between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain, which develops into its stem form out of the middle of the brain. Brainstem gliomas develop in the brain stem that connects the base of the brain to the spinal cord, just above Gliomas are a large, diverse group of brain tumours that develop from glial cells, which have a range of supportive roles within the brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
